Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 181–192 of 1131 results
Biotech: Total Cholesterol Reagents-biochemistry
🔬 1. CHOD-PAP Method (Gold Standard)
Principle
-
Cholesterol esterase converts cholesterol esters → free cholesterol
-
Cholesterol oxidase converts cholesterol → cholest-4-en-3-one + H₂O₂
-
Peroxidase (POD) uses H₂O₂ to produce a colored dye
-
Common chromogens: 4-AAP, TOOS, DAOS, HDAOS
-
Absorbance: measured at 500–550 nm depending on chromogen.
What the Reagents Contain
R1 (Buffer / Chromogen)
-
Good’s buffer (e.g., PIPES, TES)
-
Phenol or TOOS/DAOS derivatives
-
Stabilizers & surfactants
-
Preservatives
R2 (Enzyme Reagent)
-
Cholesterol esterase
-
Cholesterol oxidase
-
Peroxidase
-
Additional surfactants
Biotech: Triglycerides (TG) Reagents- biochemistry
🔬 1. Szasz Method (Standard for GGT)
Principle
GGT catalyzes the transfer of the γ-glutamyl group from a synthetic donor substrate to an acceptor molecule.
Reaction: L-γ-glutamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide
-
Glycylglycine
→ 5-amino-2-nitrobenzoate (colored product) -
γ-glutamyl-glycylglycine
The rate of formation of 5-amino-2-nitrobenzoate is measured kinetically.
Measurement
-
Absorbance: 405–410 nm
-
Mode: Kinetic, multiple readings (rate method)
-
Proportional to: GGT activity (U/L)
Biotech: Urea Reagents-biochemstry
Principle of Measurement
1. Urease–GLDH Method (Enzymatic UV)
(Most widely used, highly specific)
How it works:
-
Urease enzyme hydrolyzes urea → ammonia + carbon dioxide.
-
Ammonia reacts with α-ketoglutarate in the presence of GLDH (glutamate dehydrogenase).
-
NADH is oxidized to NAD⁺, causing a decrease in absorbance at 340 nm.
-
The rate of absorbance decrease is proportional to urea concentration.
Advantages:
-
Very specific
-
Minimal interference
-
Ideal for automated chemistry analyzers
2. Berthelot (Indophenol) Colorimetric Method
(Common in semi-auto analyzers)
How it works:
-
Urease converts urea to ammonia.
-
Ammonia reacts with phenol and hypochlorite → blue indophenol dye.
-
Absorbance measured at 580–600 nm.
Advantages:
-
Stable color formation
-
Suitable for manual and semi-automatic systems
3. Diacetyl Monoxime (DAM) Method (Older method)
Forms a yellow complex; used mainly in research.
Reagent Components
Urease–GLDH Reagents May Contain:
-
Urease enzyme
-
GLDH enzyme
-
NADH
-
α-ketoglutarate
-
Buffer solution
-
Surfactants and stabilizers
-
Preservatives
Berthelot Reagents May Contain:
-
Phenol
-
Sodium nitroprusside
-
Hypochlorite
-
Buffer solution
Packaging Formats
-
Two-reagent systems (R1 buffer + R2 enzyme)
-
Single-reagent kits (less common)
-
Analyzer-specific liquid cartridges
Typical volumes: 25 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml, 250 ml.
Biotech: Uric Acid Reagents-biochemistry
Principle of Measurement
1. Uricase–Peroxidase (Uricase/POD) Method (Most common)
Reaction Process
-
Uricase converts uric acid into allantoin, CO₂, and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
-
H₂O₂ reacts with a chromogenic dye in the presence of peroxidase, forming a colored quinone-imine or similar compound.
-
The color intensity is measured photometrically between 520–550 nm, proportional to uric acid concentration.
Advantages:
-
High specificity
-
Minimal interference from glucose, ascorbate, and bilirubin (depending on kit formulation)
-
Widely compatible with automated analyzers
Reagent Components
A typical uric acid reagent kit contains:
R1 (Buffer/Enzyme reagent)
-
Phosphate buffer
-
Uricase enzyme
-
Peroxidase enzyme
-
Chromogenic dye precursors
-
Surfactants and stabilizers
-
Preservatives
R2 (Color reagent) (in two-reagent systems)
-
Dye enhancer or color-developing components
-
Auxiliary stabilizers
-
Preservatives
Some kits come as single ready-to-use reagent.
Packaging Formats
-
Liquid-stable reagents (most common)
-
Two-reagent packs (R1 + R2)
-
Analyzer-specific cartridges
-
Optional calibrators and controls
Common volumes: 25 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml, 250 ml, and larger bulk sizes.
Sample Types
-
Serum
-
Plasma (heparin, EDTA)
-
Urine (usually diluted before measurement)
BIOWAY URS-10H Reagent Strips for Urinalysis
BiPAP Machine Ventmed
BiPAP Machine (Ventmed) is a medical device designed to assist people with breathing difficulties—especially those with conditions like COPD, severe sleep apnea, or other respiratory insufficiencies. BiPAP stands for Bi‑level Positive Airway Pressure, meaning it provides two different pressures: a higher pressure when you breathe in (inhale) and a lower pressure when you breathe out (exhale). This makes breathing easier and more natural compared to a standard CPAP machine.
🌬️ How It Works
-
Inhalation Support: The machine delivers a higher pressure to help open the airway and assist lung inflation.
-
Exhalation Ease: It lowers the pressure during exhalation so breathing out feels more comfortable and less effortful.
🫁 Who It Helps
BiPAP is especially useful for people who:
-
Have COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
-
Need extra ventilatory support
-
Experience difficulty exhaling against pressure
-
Have advanced sleep apnea requiring variable pressure
-
Recovering from certain respiratory conditions
🔑 Key Benefits
-
Eases both inhaling and exhaling
-
Improves oxygenation and ventilation
-
Reduces work of breathing
-
Supports better sleep and respiratory function
-
Often adjustable to suit individual needs
⚙️ Common Features
-
Adjustable pressure settings
-
Comfort‑oriented design
-
Some models include humidification
-
Easy controls and clear display
The Ventmed BiPAP Machine combines effective respiratory support with patient comfort, helping users breathe more easily whether at night, during recovery, or as part of chronic care.
Black Gloves (Food Handling Gloves)
Black Top Vacutainer
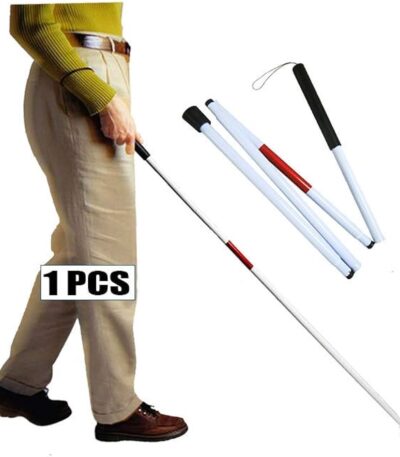
Blind Walking Stick (White Cane)
Description
-
Material: Lightweight aluminum or fiberglass for easy handling
-
Color: Predominantly white for high visibility, often with a red lower section
-
Design:
-
Straight or foldable (3–5 fold sections)
-
Elastic cord inside for smooth folding/unfolding
-
-
Grip:
-
Ergonomic rubber or foam handle for comfort
-
-
Tip:
-
Various replaceable tips (rolling tip, marshmallow tip, pencil tip)
-
Made from durable plastic or nylon
-
-
Length: Typically between 110–150 cm depending on user height
Blood Bank Fridge
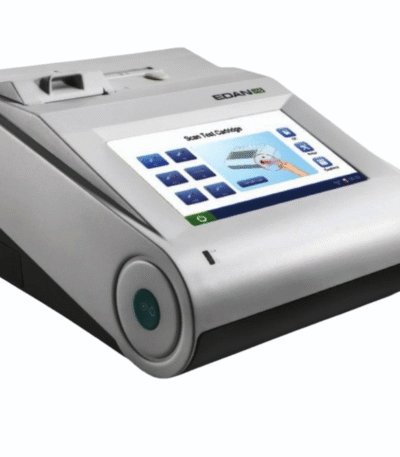
Blood Gas and Chemistry Analyzer (Edan – i15)
- Portable and Lightweight: Weighs only about 3.65 kg (8.05 lb), with a built-in rechargeable battery allowing for up to 50 continuous tests, making it highly mobile for bedside use.
- Easy to Use: Features an intuitive 7-inch color LCD touch screen and a simple, three-step operation procedure (sample collection, mixing, and introduction).
- Maintenance-Free: The use of disposable test cartridges and calibrant fluid packs eliminates the need for routine maintenance, gas cylinders, and minimizes biohazard risks.
- Fast Results: Provides results in as little as 35 seconds to one minute after sample aspiration, enabling quick clinical decisions.
- Data Management: Capable of storing up to 10,000 patient data points and supports seamless integration with Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) or Hospital Information Systems (HIS) via wired (USB, RS232) or wireless (WLAN) networking.
- Built-in Quality Control: Ensures accuracy and reliability through internal quality control mechanisms, an electronic simulator, and liquid quality control solutions.
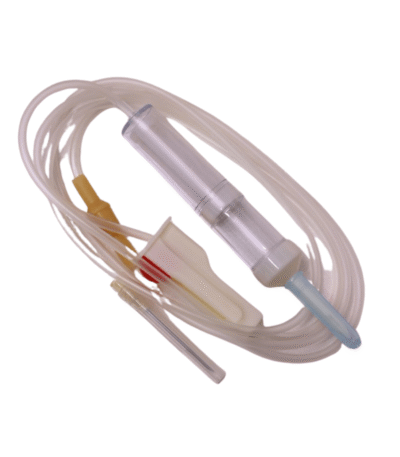
Blood Giving Set – 25s
Key Features
-
Drop factor: 25 drops/mL (medium-drip for controlled transfusion).
-
Wide-bore tubing – reduces hemolysis and allows smooth blood flow.
-
In-line blood filter (usually 170–200 microns) – removes clots and debris.
-
Drip chamber – designed for safe dripping of blood without excessive frothing.
-
Roller clamp – controls flow rate.
-
Air vent (on some sets) – used when transfusing from a glass bottle.
-
Spike + Luer connector – attaches to the blood bag and the patient’s cannula.