Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 145–156 of 1131 results
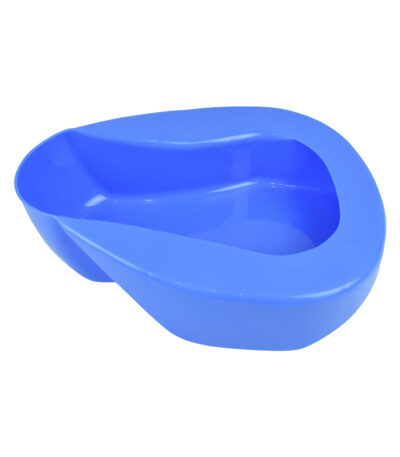
Bed Pan ( Plastic)
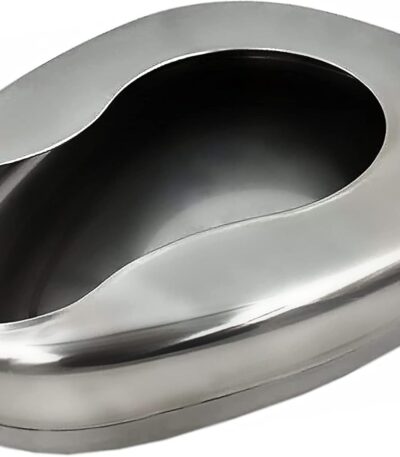
Bed Pan (Metallic)
A metallic bed pan is a reusable toileting aid designed for patients who are bedridden or have limited mobility. It allows patients to urinate or defecate while remaining in bed, providing convenience and maintaining hygiene in hospitals, nursing homes, or home care settings.
Description
-
Material: Durable stainless steel or enameled metal for long-lasting use
-
Design: Anatomically shaped to fit comfortably under the patient
-
Capacity: Typically holds enough volume for urine and stool collection
-
Edges: Smooth, rounded edges to prevent discomfort and injury
-
Handles: Some models include handles for easy positioning and removal
-
Cleaning: Sterilizable and easy to disinfect after use
-
Dimensions: Standard size suitable for adult patients
Key Features
-
Strong, durable, and long-lasting
-
Easy to clean and sterilize
-
Smooth edges for patient comfort
-
Resistant to corrosion and wear
-
Can be used for both urine and feces collection
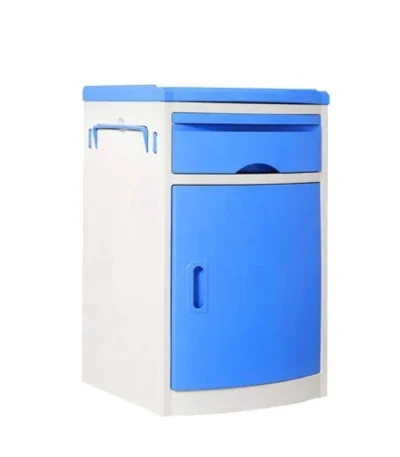
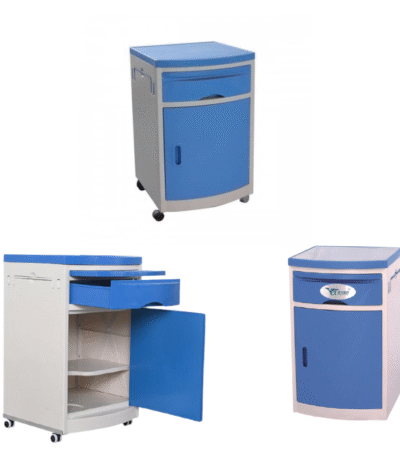
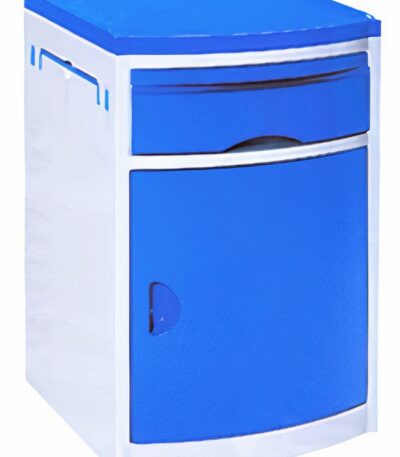
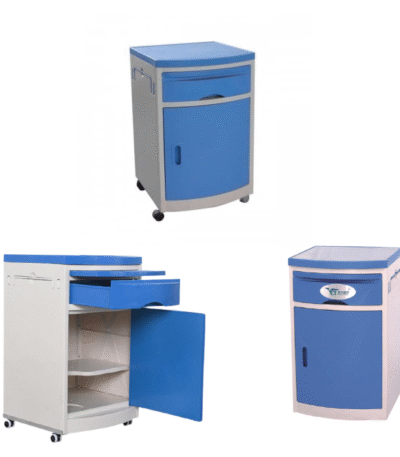
Bed Side Lockers
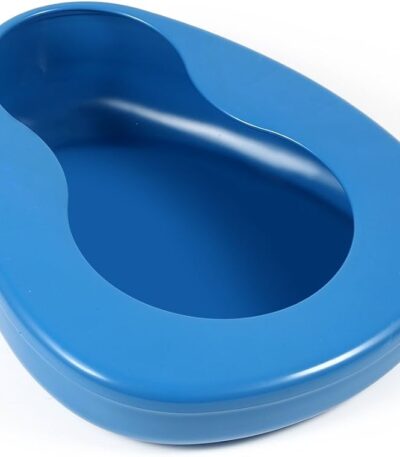
Bedpan
Bedside Locker
A bedside locker is a small storage unit placed beside a hospital bed, designed to keep a patient’s personal belongings and essential medical items within easy reach. It is a standard piece of hospital furniture found in wards, patient rooms, and recovery areas.
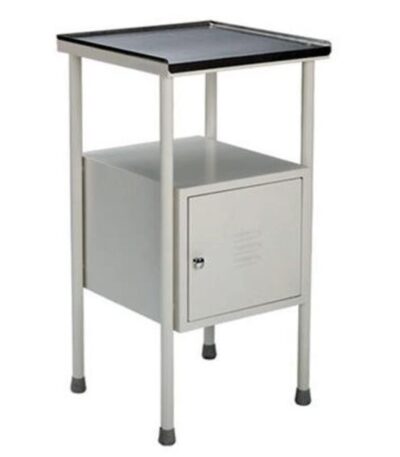
BEDSIDE LOCKER
>Machine
pressed sheet
box with
lockable doors.
>Assembled to
CRC tubular
legs fitted with
PVC stumps.
>Stainless
steel top.
Bedside Locker
The Hospital Bedside Locker is a compact and functional storage unit designed for patient convenience and hospital efficiency. It is placed beside the patient’s bed to store personal items, medicines, and hospital supplies. Made from high-quality steel or ABS plastic, it ensures durability, hygiene, and easy maintenance in demanding healthcare environments.
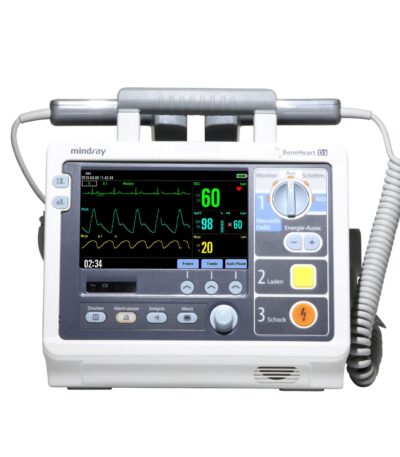
BeneHeart Defibrillator (by Mindray)
The BeneHeart series — including models such as D3, D6, and D30 — delivers biphasic defibrillation shocks with adjustable energy levels up to 360 joules, ensuring effective cardiac resuscitation for adults and children. It uses impedance-compensated technology that automatically adjusts the shock energy to match the patient’s body resistance, improving success rates during cardiac arrest management.
The unit is equipped with a bright color display, intuitive controls, and built-in safety features that allow clinicians to operate it quickly and confidently during emergencies. It also supports data storage, review, and transfer, making it suitable for both hospital and field applications.
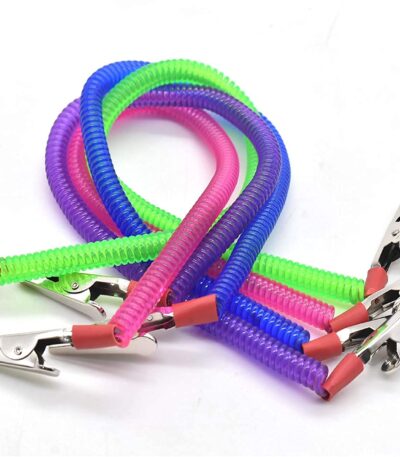
Bib Holder (Dental Bib Clip / Chain Holder)
A Bib Holder is a dental accessory used to secure patient bibs or napkins around the patient’s neck during dental procedures. It ensures that the bib stays in place and protects the patient’s clothing from water, saliva, and debris.
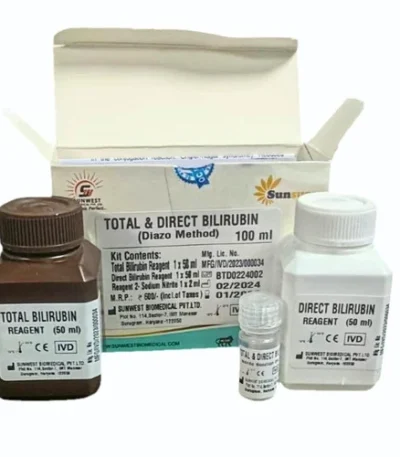
Bilirubin – Total & Direct
🔬 1. Direct Bilirubin (Conjugated) — Diazo Method
Principle
Direct (conjugated) bilirubin reacts directly with diazotized sulfanilic acid to form azobilirubin, a reddish-purple complex.
-
Absorbance: ~540–560 nm
-
Method: Endpoint or timed endpoint
-
No accelerator needed (only conjugated bilirubin reacts)
Reagent Components
-
Sulfanilic acid
-
Sodium nitrite
-
Hydrochloric acid (for diazo formation)
-
Buffer (acetate)
-
Preservatives
Some manufacturers supply:
-
R1: Buffer
-
R2: Diazo reagent
🧪 2. Total Bilirubin — Diazo Method (Accelerated)
Principle
Unconjugated bilirubin requires an accelerator to react with the diazo reagent.
Common accelerators:
-
Caffeine–benzoate
-
Surfactants
-
Methanol or DMSO (older methods)
Total bilirubin reacts with diazo reagent to form azobilirubin.
-
Absorbance: ~540–560 nm
-
Method: Endpoint or timed endpoint
Reagent Components
-
Caffeine-benzoate accelerator
-
Sulfanilic acid
-
Sodium nitrite
-
Acid buffer
-
Stabilizers and preservatives
Formats:
-
1-reagent systems (common today)
-
2-reagent systems (R1 accelerator + R2 diazo reagent)
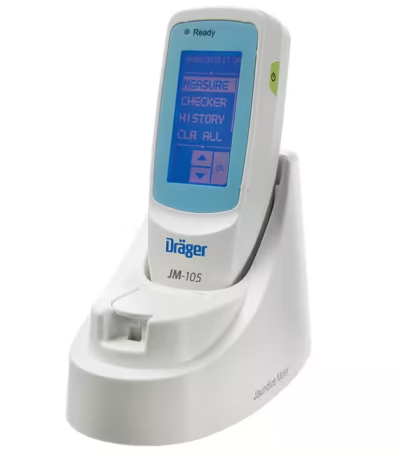
Bilirubinometer
A bilirubinometer is a medical diagnostic device used to measure the level of bilirubin in newborns (and sometimes adults) to identify and monitor jaundice
There are two main types:
-
Transcutaneous bilirubinometers: Non-invasive devices that estimate serum bilirubin by shining light onto the baby’s skin (often the forehead, sternum, or ear).
-
Serum bilirubinometers: Use a small blood sample and laboratory optics or photometry to give a direct bilirubin reading.
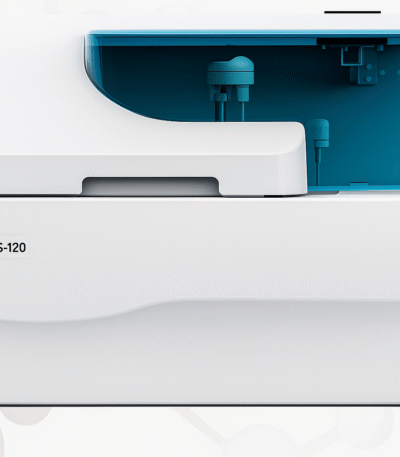
BIOELAB AS‑120 Fully Automatic Clinical Chemistry Analyzer / AS‑120 Auto Biochemistry Analyzer
Key Features & Specifications
-
Type: Fully automatic, random-access chemistry analyzer with open reagent system (can use reagents from different suppliers).
-
Throughput: Approximately 120 tests per hour.
-
Reagent capacity: Typically around 80 positions (40 for R1 + 40 for R2) with ~40 sample positions.
-
Reaction cuvettes: Around 50 cuvettes; reaction volume ~150 µL to ~330 µL.
-
Optical system: Multi-wavelength detection (340 nm, 405 nm, 450 nm, 505/510 nm, 546 nm, 578 nm, 630 nm, 700 nm).
-
Reagent tray cooling: Continuous cooling system maintaining 2 °C–14 °C.
-
Sample & reagent probe features: Liquid level detection, collision protection, automatic probe cleaning and adjustment.
-
Calibration & quality control: Supports linear and nonlinear calibration, multi-point calibration, Westgard QC plotting.
-
Physical footprint: Approximately 750 mm × 550 mm × 490 mm; weight ~70 kg.