Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 1033–1044 of 1124 results
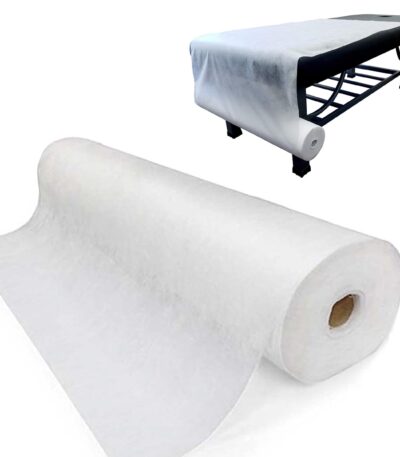
Tissue Bed Spread
-
Purpose & Use
-
A tissue bed spread is a surgical instrument or device used to hold tissues apart during surgery, providing a clear and stable view of the surgical site.
-
Commonly used in general surgery, orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, and other procedures where precise exposure is required.
-
It helps protect surrounding tissue while giving the surgeon easy access to the target area.
-
-
Structure & Components
-
Typically made of high-quality stainless steel, which is durable, corrosion-resistant, and easy to sterilize.
-
May consist of two or more arms/blades that can be adjusted to separate tissue.
-
Some designs include ratchets or locking mechanisms to maintain tension without constant manual holding.
-
-
Types & Variations
-
Hand-held retractors: simple blades held manually to separate tissue.
-
Self-retaining tissue spreaders: stay in place without the need for an assistant, often with ratchet locks.
-
Specialized designs: certain procedures may require curved or angled blades to fit specific anatomical sites.
-
-
Advantages
-
Provides excellent exposure of the operative field.
-
Reduces tissue trauma compared to manual retraction.
-
Frees up an assistant, as self-retaining models hold tissues in place independently.
-
Enhances precision and safety during delicate procedures.
-
-
Safety & Handling
-
Must be properly sterilized before use to prevent infection.
-
Care must be taken to avoid excessive tension, which can damage tissue.
-
Surgeons should select the appropriate size and type based on the tissue and procedure.
-
-
Common Uses
-
Abdominal or thoracic surgeries for organ exposure.
-
Orthopedic procedures to hold muscle or fascia apart.
-
Plastic and reconstructive surgery for delicate tissue manipulation.
-
Microsurgery or minor procedures where precise tissue control is critical.
-
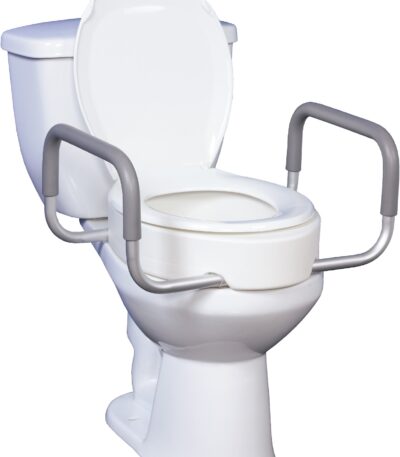
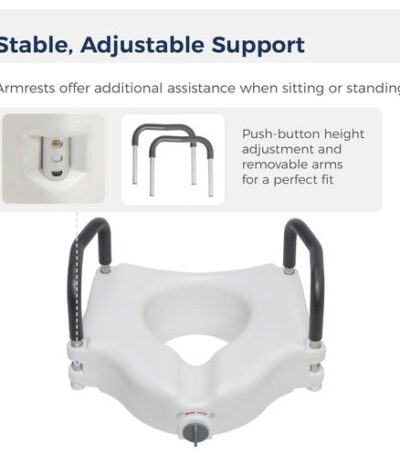
Toilet raiser
Toilet Raiser
Tongue Depressors (Pack of 100)
-
Material & Build
-
Usually made of smooth, polished wood, often birch.
-
Sanded carefully so there are no rough edges or splinters, making them safe to use in the mouth.
-
-
Shape & Size
-
Flat, broad, with rounded ends.
-
Typical size is about 6 inches (15 cm) long, 0.7 inches (1.8 cm) wide, and roughly 1.5–2 mm thick.
-
Smaller versions exist for children.
-
-
Sterility & Packaging
-
Can be non-sterile (bulk-packed) or sterile (individually wrapped).
-
A pack of 100 provides enough for multiple clinical exams or other uses.
-
-
Function / Use
-
In medicine, they are used to hold down the tongue to allow examination of the throat, mouth, and tonsils.
-
Single-use in clinical settings to maintain hygiene.
-
Also used for crafts, lab work, or beauty applications, such as mixing or stirring.
-
-
Safety & Quality
-
Smooth, splinter-free surface to prevent injury.
-
Typically odorless and tasteless, so they don’t interfere with oral exams.
-
-
Disposal & Sustainability
-
Made from natural wood, so they are biodegradable.
-
In medical settings, disposed of after one use to prevent cross-contamination.
-
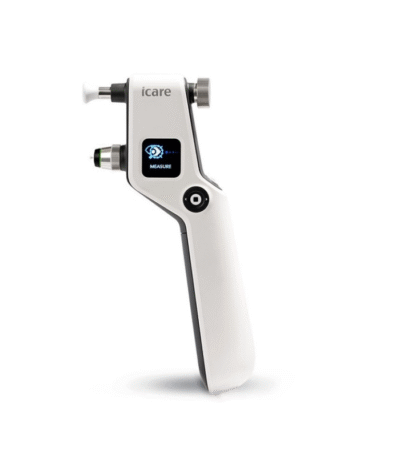
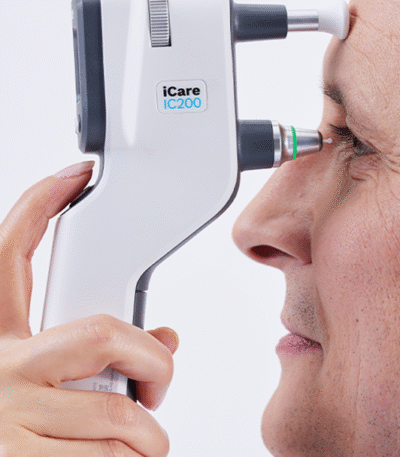
Tonometer
Topical Fluoride / Fluoride Gel
Topical Fluoride (also called Fluoride Gel) is a preventive dental agent applied directly to the tooth surface to help strengthen enamel, prevent tooth decay (dental caries), and reduce sensitivity. It is one of the most effective and widely used methods for protecting teeth in both children and adults.
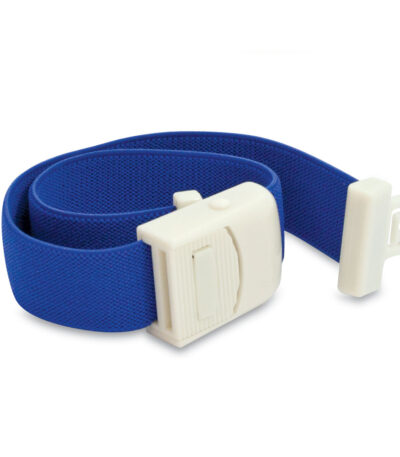
Tourniquet
Types of Tourniquets
1. Clinical / Phlebotomy Tourniquet
-
Elastic strap used when drawing blood.
-
Temporarily restricts venous return to make veins more visible.
-
Usually made of latex-free elastic material.
-
Releasable buckle or simple stretch-and-release design.
2. Emergency / Hemorrhage Control Tourniquet
-
Used to stop severe bleeding (arterial bleeding).
-
Common types:
-
CAT (Combat Application Tourniquet)
-
SOF-T
-
Windlass tourniquet
-
-
Used in trauma, combat medicine, first aid.
3. Surgical Tourniquet
-
Pneumatic (inflatable) cuff used to control blood flow during orthopedic or vascular surgery.
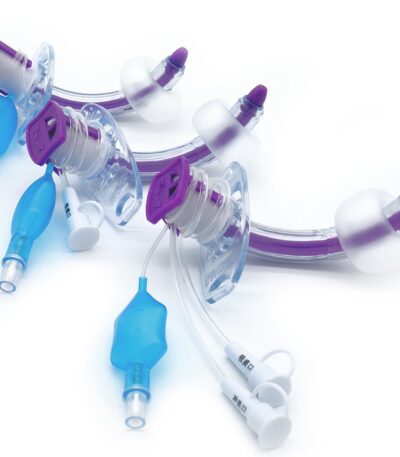
Trachaestomy tube sizes 6.5,7.5,8.0,7.0
1. Adult Tracheostomy Tube Sizes
Most common adult sizes:
| Patient Type | Common Internal Diameter Sizes |
|---|---|
| Adult Female | Size 6.0, 7.0 |
| Adult Male | Size 7.0, 8.0 |
| Large Adult | Size 8.0, sometimes 9.0 |
Key point:
-
Adult sizes usually range from 6.0 to 9.0 mm internal diameter (ID).
2. Pediatric Tracheostomy Tube Sizes
Pediatric tubes are chosen based on age and weight.
| Age Group | Typical Size |
|---|---|
| Premature babies | 2.5 – 3.0 mm |
| 0–6 months | 3.0 – 3.5 mm |
| 6–12 months | 3.5 – 4.0 mm |
| 1–3 years | 4.0 – 4.5 mm |
| 3–6 years | 4.5 – 5.0 mm |
| 6–12 years | 5.0 – 6.0 mm |
| >12 years (teenagers) | 6.0 – 7.0 mm |
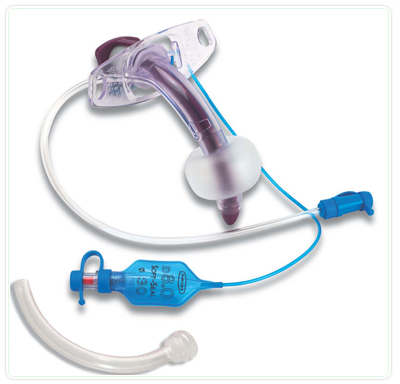
Tracheostomy Tube – Sizes 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0
A Tracheostomy Tube is a curved, hollow medical device inserted through a tracheostomy stoma (an opening in the neck) into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway and enable breathing, suctioning, or mechanical ventilation.
The sizes 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, and 8.0 mm refer to the internal diameter (ID) of the tube, typically used for adult patients of different anatomical builds.
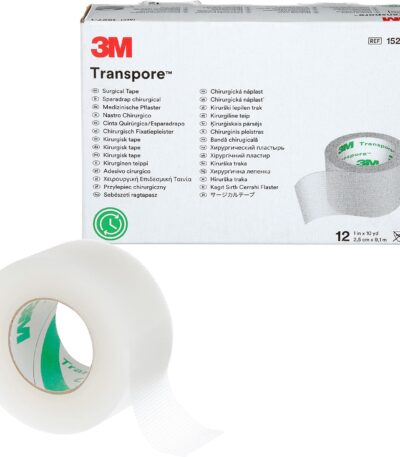
Transpore Tape 1″ × 12 Rolls
Transpore tape is a transparent, hypoallergenic, perforated surgical tape commonly used in medical settings.
Key Features
-
Width: 1 inch
-
Quantity: 12 rolls per pack
-
Material: Transparent polyethylene
-
Perforated: Easy to tear by hand (no scissors needed)
-
Hypoallergenic: Gentle on most skin types
-
Adhesion: Strong grip but easy to remove
-
Uses:
-
Securing dressings and bandages
-
Fixing IV lines and tubing
-
Wound care
-
General clinical use
-
Benefits
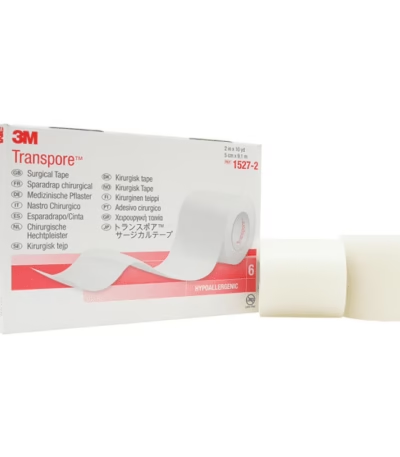
Transpore Tape 2″ × 6 Rolls
Transpore tape is a transparent, perforated, hypoallergenic surgical tape widely used in medical settings.
Key Features
-
Width: 2 inches
-
Quantity: 6 rolls per pack
-
Material: Transparent polyethylene film
-
Perforated: Easily tears by hand (no scissors needed)
-
Hypoallergenic: Gentle on most skin types
-
Strong Adhesion: Secure but still easy to remove
-
Water-resistant & breathable
Common Uses
-
Securing dressings, bandages, and gauze
-
Fixing IV tubing, catheters, and medical devices
-
Wound care
-
General hospital and clinical applications