Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 493–504 of 1124 results
Finecare T4 Rapid Quantitative Test immunoassay
✅ Key Features & Specifications
-
Test principle: Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA) for the quantitative measurement of Total Thyroxine (T4) in human serum, plasma, or whole blood.
-
Analyte: Total T4 (TT4).
-
Measurement range: Typically 2–18 µg/dL (may vary slightly depending on lot).
-
Sample types: Whole blood, serum, or plasma.
-
Sample volume: Approximately 75–100 µL per test.
-
Turnaround time: Results available in 15 minutes.
-
Storage conditions: Test cartridges stable at 4 °C – 30 °C, with a shelf life up to 24 months.
-
Instrument compatibility: Requires a Finecare™ Fluorescence Immunoassay Analyzer (Finecare, Finecare Plus, or Finecare II) for quantitative reading.
Finecare Testosterone Rapid Quantitative Test Kit immunoassay
Key Features and Specifications
-
Test Principle: Fluorescence immunoassay.
-
Sample Type: Serum, plasma, or whole blood.
-
Measuring Range: Typically 0.1 – 15 ng/mL (may vary with analyzer model).
-
Reaction Time: Approximately 15 minutes.
-
Sample Volume: About 75 µL.
-
Storage Temperature: 4°C – 30°C.
-
Shelf Life: Valid until the indicated expiry date.
-
Compatible Analyzer: Finecare FIA Analyzer (e.g., Finecare FS-113, Finecare Plus).
Finecare Total IgE Rapid Quantitative Test Kit immunoassay
Key Features and Specifications
-
Test Principle: Fluorescence immunoassay.
-
Sample Type: Serum, plasma, or whole blood.
-
Measuring Range: Typically 10 – 2000 IU/mL (depending on analyzer model).
-
Reaction Time: Approximately 15 minutes.
-
Sample Volume: About 75 µL.
-
Storage Temperature: 4°C – 30°C.
-
Shelf Life: Up to the indicated expiry date.
-
Compatible Device: Finecare FIA Analyzer (e.g., Finecare FS-113, Finecare Plus).
Finecare TSH Rapid Quantitative Test immunoassay
✅ Key Features & Specifications
-
Test principle: Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA) for the quantitative measurement of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) in human serum, plasma, or whole blood.
-
Analyte: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
-
Measurement range: Typically 0.1–100 µIU/mL (may vary slightly depending on the lot).
-
Sample types: Whole blood, serum, or plasma.
-
Sample volume: Approximately 75–100 µL per test.
-
Turnaround time: Results available in 15 minutes.
-
Storage conditions: Test cartridges stable at 4 °C – 30 °C, with a shelf life up to 24 months.
-
Instrument compatibility: Requires a Finecare™ Fluorescence Immunoassay Analyzer (Finecare, Finecare Plus, or Finecare II) for quantitative reading.
Finecare TSH/T3/T4 Control Kit
Finecare Vitamin B12 Rapid Quantitative Test Kit
Finecare Vitamin D Rapid Quantitative immunoassay
✅ Key Features & Specifications
-
Test principle: Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA) for the quantitative measurement of 25-hydroxy Vitamin D [25(OH)D] in human serum, plasma, or whole blood.
-
Analyte: 25-hydroxy Vitamin D (25(OH)D).
-
Measurement range: Typically 4–100 ng/mL (may vary slightly depending on the lot).
-
Sample types: Whole blood, serum, or plasma.
-
Sample volume: Approximately 75–100 µL per test.
-
Turnaround time: Results available in 15 minutes.
-
Storage conditions: Test cartridges stable at 4 °C – 30 °C, with a shelf life up to 24 months.
-
Instrument compatibility: Requires a Finecare™ Fluorescence Immunoassay Analyzer (Finecare, Finecare Plus, or Finecare II) for quantitative reading.
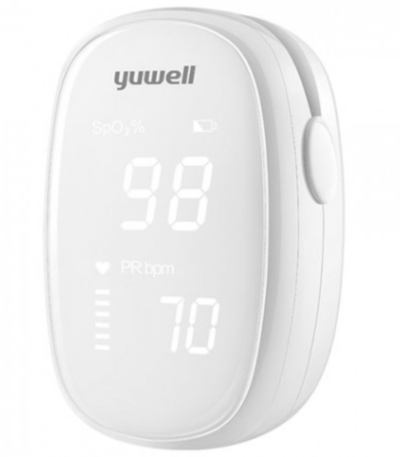
Fingertip Pulse Oximeter
Fingertip pulse oximeter used for monitoring of oxygen saturation and heart rate.
Easy to use, lightweight and portable.
Bright led display.
Finishing Strips
Description:
Finishing Strips are thin, flexible abrasive strips used in dentistry for finishing, contouring, and polishing interproximal surfaces of composite restorations and enamel. They help achieve smooth contact areas and restore natural tooth anatomy.
First Aid Kit
Fissure Sealant
A Fissure Sealant is a tooth-colored, resin-based protective coating applied to the pits and fissures (grooves) of premolars and molars to prevent dental caries (tooth decay). It acts as a physical barrier, sealing deep grooves where food particles and bacteria often accumulate and are difficult to clean with brushing alone.
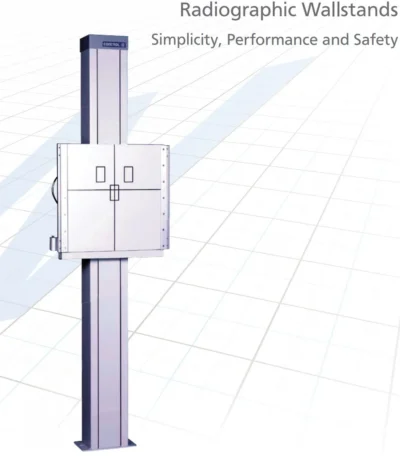
Floatex X-ray unit 500mA System with Chest Stand and Standex Vertical Bucky Wall Stand- AMI
🛠 Considerations / What to check
When procuring a system like this in Nairobi/Kenya, here are some practical points:
-
Power supply & site requirements: Many 500 mA systems require 3-phase mains (e.g., 380-440 V) and proper installation of rails, tube stand, shielding. For example, specs mention “three phase (380-440 VAC) mains supply”. s3.nl.geostorage.net
-
Room size & layout: Ensure adequate space for chest stand upright exposures, wall stand movement, table + tube travel.
-
Integration with digital imaging: If you plan DR or CR rather than film, check compatibility of generator, panel, bucky, etc.
-
After-sales service / parts: Ensure that brand/model has local service ability or spare parts availability.
-
Radiation shielding & safety compliance: Lead-lined walls/doors, bucky grid specs, dose monitoring. Some tenders specify accessories like lead apron, thyroid guard, etc. s3.nl.geostorage.net
-
Warranty / training: Installation, commissioning, user training and maintenance should be included.
-
Cost: One listing shows price ~ KSh 2,422,060 for this system in Kenya.