Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 421–432 of 1131 results
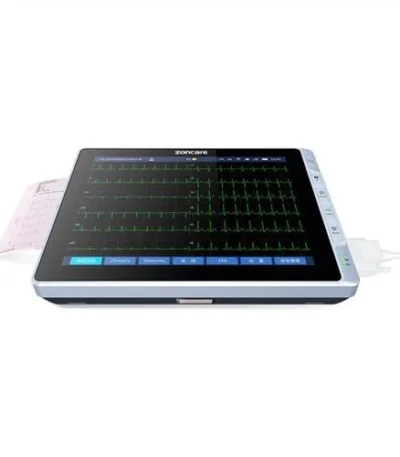
Electrocardiograph (ECG) 6 Channel
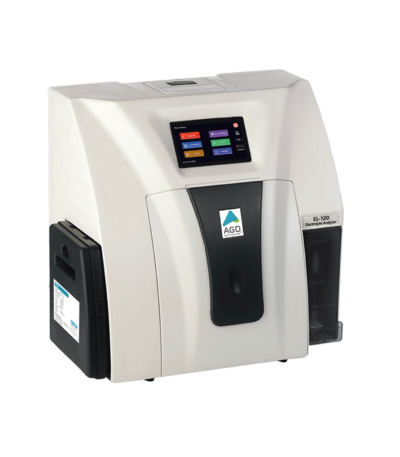
Electrolyte Analyzer Erma EL-120 (or AGD Erma EL-120)
✅ Key Features & Specifications
Measured parameters / Principle:
-
Measures ions: Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻, iCa⁺⁺ (and sometimes Li⁺ or pH) using Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) technology.
-
Sample types: whole blood, serum, plasma, urine (and occasionally CSF).
Performance & workflow:
-
Sample volume: approximately 90–100 µL.
-
Analysis time: less than 60 seconds per sample.
-
Throughput: up to 60 samples per hour.
-
Calibration: automatic two-point calibration every 4, 8, or 12 hours (user-selectable) and optional one-point calibration per sample.
-
Built-in quality control: includes tri-level QC, 30-day QC history, and Levey–Jennings (L-J) plots for QC trend monitoring.
Display & Interface:
-
5-inch colour LCD touchscreen (approx. 480 × 272 resolution).
-
Built-in thermal printer (48 mm paper width, 42 characters).
-
Interfaces: USB ports (for keyboard, mouse, barcode reader, or flash drive) and RS-232 serial port.
Physical & Environmental:
-
Dimensions: around 365 × 255 × 375 mm (some variants 395 × 260 × 375 mm).
-
Weight: roughly 5 – 7.5 kg depending on model.
-
Operating conditions: 15 – 35 °C ambient temperature, ≤ 85 % relative humidity (non-condensing).
-
Power: 100 – 240 VAC ± 10 %, 50/60 Hz.
Performance precision (typical):
-
Coefficient of variation (CV %) — Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻ ≤ 2 %; iCa⁺⁺ ≤ 3 %.
Electrophoresis Machine
Purpose
Electrophoresis is mainly used to:
Analyze DNA or RNA fragments
Study proteins and enzymes
Compare genetic samples
Check the purity or size of biomolecules
Principle of Operation
The machine works on the principle that charged particles move in an electric field:
Negatively charged molecules (like DNA) move toward the positive electrode (anode)
Smaller molecules move faster through a gel than larger ones
The gel acts as a molecular sieve
Main Components
Power Supply
Provides controlled voltage and current
Determines the speed of molecule movement
Electrophoresis Chamber (Tank)
Holds the gel and buffer solution
Contains electrodes at each end
Gel Medium
Commonly agarose (for DNA/RNA) or polyacrylamide (for proteins)
Has small pores that separate molecules by size
Buffer Solution
Conducts electricity
Maintains stable pH and temperature
Sample Wells
Small holes in the gel where samples are loaded
Electrodes
Create the electric field that drives molecule movement
Working Process
The gel is prepared and placed in the chamber
Samples are loaded into wells
Buffer is added to cover the gel
Power is switched on
Molecules migrate through the gel
Separated bands are visualized using stains or dyes
Elektro Genesis single-use syringes 2cc
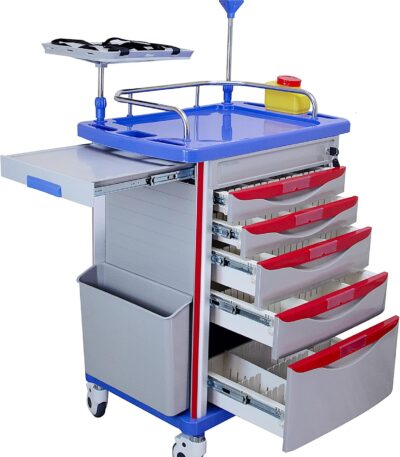
Emergency Crash Cart
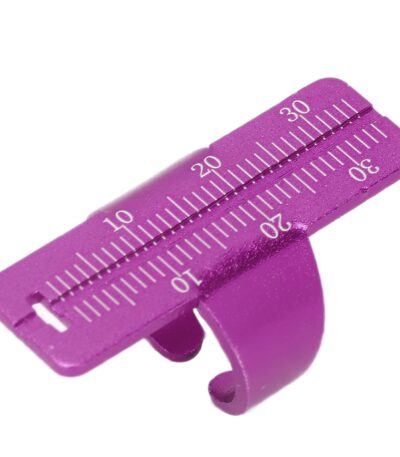
Endo Rulers (Endodontic Rulers / Measuring Gauges)
An Endo Ruler is a measuring device used in endodontics (root canal treatment) to accurately determine the working length of endodontic instruments such as files, reamers, and spreaders before or during procedures. It ensures that instruments reach the correct length inside the root canal without extending beyond the apex.
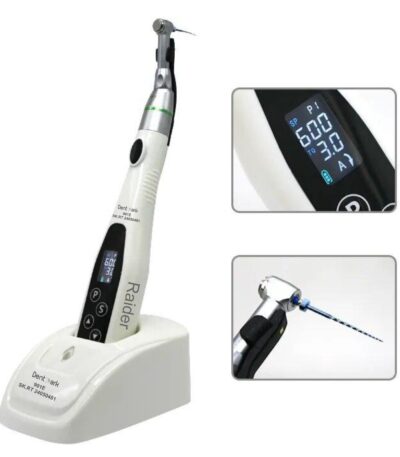
Endomotor
An Endomotor is a dental rotary device used during root canal treatment (RCT) to mechanically drive endodontic files inside the root canal system. It helps in cleaning, shaping, and preparing the canals efficiently and safely, offering speed control, torque adjustment, and automatic reverse motion to prevent file breakage.
It is an essential instrument in modern endodontics, providing better precision and comfort compared to manual filing.
Endotracheal Tube
A bogie tube (often called a bougie tube or intubation bougie) is a long, flexible guiding tool used by healthcare professionals to help place an endotracheal tube into a patient’s airway when breathing support is urgently needed. It acts like a gentle “pathfinder,” especially in difficult situations where the airway is hard to see or access.
The tube is slim, smooth, and bendable, allowing it to slide carefully through the vocal cords and into the windpipe. Once it’s in the correct position, the endotracheal tube is simply passed over it and guided smoothly into place. This method increases safety, accuracy, and speed—especially during emergencies, swelling, trauma, or when visibility is limited.
Because of its flexibility and touch-sensitive tip, providers can feel subtle “tracheal clicks” or resistance, which helps confirm the bougie is properly placed. This makes the bogie tube a trusted, life-saving tool that supports safe airway management and helps ensure the patient receives oxygen quickly and effectively.
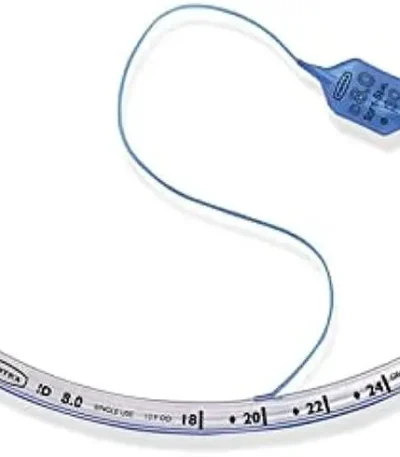
Endotracheal Tube (ET Tube) – All Sizes
An Endotracheal Tube (ET Tube) is a flexible plastic tube inserted through the mouth or nose into the trachea to maintain an open airway, deliver oxygen or anesthetic gases, and assist in mechanical ventilation.
It is one of the most essential devices in anesthesia, intensive care, and emergency medicine.
Endotracheal Tube Stylet (Sizes 10, 14, 15)
An Endotracheal Tube Stylet is a malleable metal or plastic-coated wire used to shape and stiffen an endotracheal tube (ETT) during intubation. It allows the clinician to guide the ETT smoothly into the trachea, especially in difficult airway situations or when visualization is limited.
Endozime Premium
ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) Surgical Set
Typical Components and Their Uses
1. Diagnostic and Examination Instruments
-
Head Mirror / Headlight: Provides illumination during examination and surgery.
-
Tongue Depressor: Used to hold the tongue down during throat examination.
-
Nasal Speculum: For widening the nasal passage to allow better visualization.
-
Ear Speculum: Used to examine the ear canal and tympanic membrane.
-
Laryngeal Mirror: Helps visualize the larynx and vocal cords.
2. Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
-
Scalpels and Blades: For making precise incisions.
-
Metzenbaum Scissors: For fine tissue dissection.
-
Iris Scissors: For delicate cutting tasks in confined spaces.
-
Mastoid Gouge and Chisel: Used in ear surgeries involving bone removal.
3. Grasping and Holding Instruments
-
Alligator Forceps: For removing foreign bodies from the ear or nasal cavity.
-
Tilley Nasal Forceps: Used to hold nasal packs or dressings.
-
Tonsil Forceps: For gripping tonsillar tissue during tonsillectomy.
-
Kocher and Allis Forceps: For holding and manipulating tissue securely.
4. Retracting and Exposing Instruments
-
Mouth Gag (Davis or Boyle-Davis): Keeps the mouth open during throat surgery.
-
Tongue Retractor: Used to pull and stabilize the tongue.
-
Nasal Retractors: To provide exposure within nasal cavities.
5. Suction and Irrigation Instruments
-
Yankauer Suction Tube: Removes fluids and maintains a clear operative field.
-
Frazier Suction Tip: Provides precision suction in delicate areas like the ear canal.
6. Clamping and Hemostatic Instruments
-
Mosquito and Kelly Forceps: Used to clamp small blood vessels and control bleeding.
-
Tonsil Artery Forceps: Specially designed for securing vessels in tonsillar surgeries.
7. Miscellaneous Instruments
-
Ear Curettes: For removing wax or tissue debris from the ear canal.
-
Myringotomy Knife: Used to make incisions in the eardrum.
-
Probe and Hook Set: For exploring and manipulating delicate structures.
-
Suture Needle Holder: For suturing delicate tissues.