Filter by price
Stock status
Showing 109–120 of 1131 results
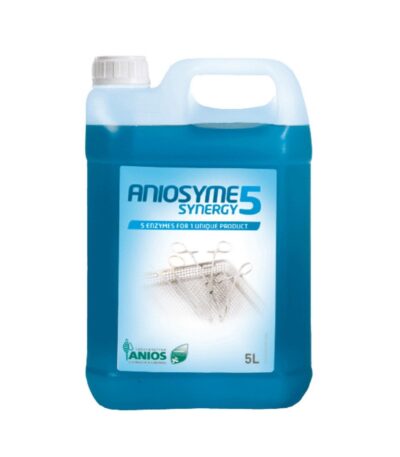
Aniosyme-5litres
Aniosyme is an enzymatic detergent solution used for cleaning and pre-disinfecting medical and dental instruments before sterilization. It effectively removes organic residues such as blood, tissue, saliva, and other biological materials that can interfere with sterilization.
It is produced by Laboratoires Anios, a company known for manufacturing infection control and disinfection products used in healthcare facilities.
Ankle and Wrist Weights
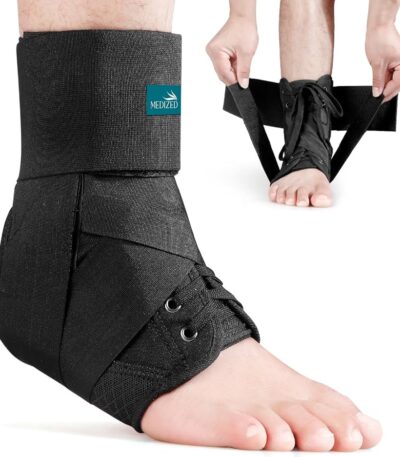
Ankle Brace With Adjustable Laces
An ankle brace with adjustable laces is a sturdy support designed to keep your ankle stable and protected, especially after a sprain, strain, or when dealing with weak joints. It works much like a high-top shoe: the lace-up design allows you to tighten or loosen the brace for a secure, personalized fit.
Made from strong yet comfortable material, the brace wraps around the ankle and limits harmful side-to-side movements while still allowing natural walking motion. Extra straps or stays may be included to add firmness and prevent the ankle from rolling.
Applicator Sticks
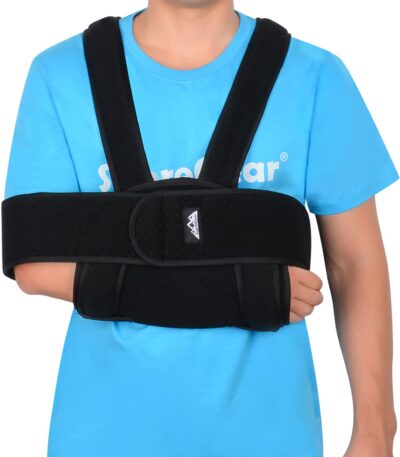
Arm Sling
Key Features:
-
Material:
Made from soft, breathable fabrics such as cotton, polyester, or mesh for comfort and ventilation. -
Adjustable Straps:
Features adjustable shoulder straps with Velcro closures to ensure proper fit and positioning. -
Padded Support:
Some models include padding at the shoulder strap or elbow area for added comfort. -
Immobilization:
Holds the arm in a flexed position close to the body to reduce movement of the elbow, wrist, and shoulder. -
Lightweight & Comfortable:
Can be worn for extended periods without causing discomfort or strain. -
Sizes:
Typically available as one-size-fits-most or in multiple sizes for adults and children.
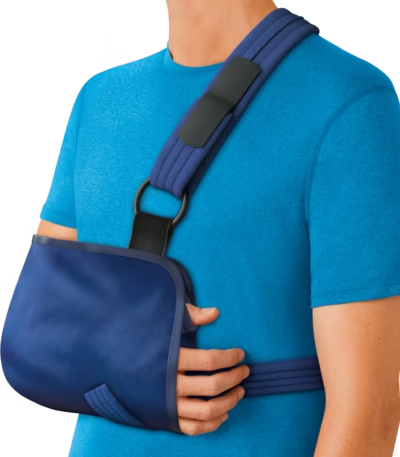
Arm Sling with Strap
An arm sling with strap is a supportive device designed to hold your arm close to your body, providing comfort and stability after an injury, surgery, or strain. The sling consists of a soft fabric pouch where your forearm rests, along with an adjustable strap that goes around your neck or shoulder to carry the weight of the arm.
This support helps reduce pain, prevent unnecessary movement, and protect the arm from accidental bumps or strain. The adjustable strap allows you to customize the fit for maximum comfort, keeping the arm elevated slightly to reduce swelling and promote proper healing.
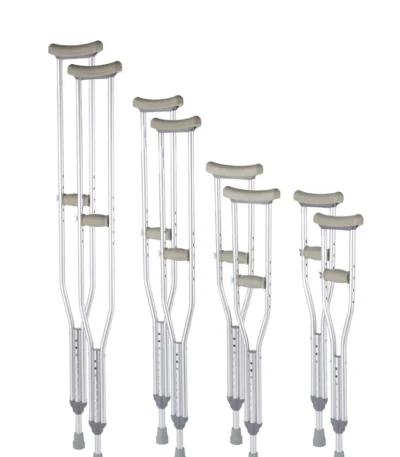
Armpit crutches
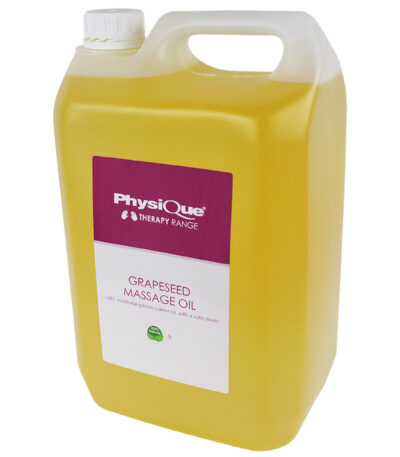
Aromatherapy Massage Oil 5 Litres
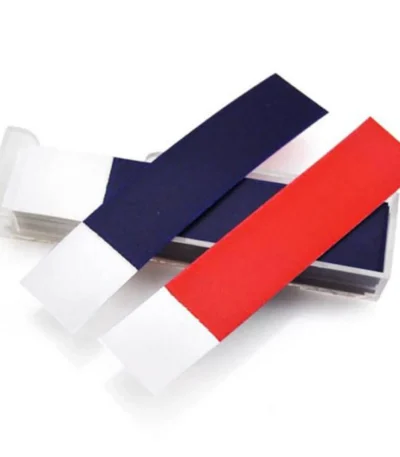
Articulating Paper
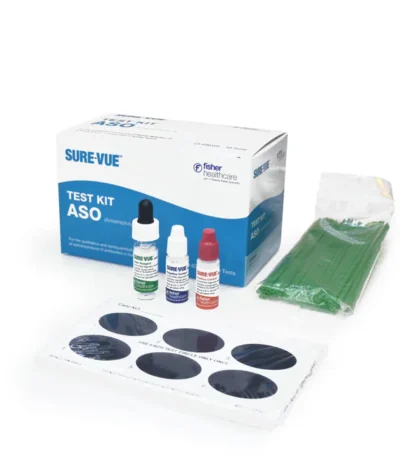
ASOT Test Kit
Specifications
| Content And Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Control Sets | Yes |
| CPT Code | 86060 |
| CE Marker | Self-declared |
| Clia Complexity | Moderate |
| Detectable Analytes | Anti-Streptolysin O (ASO) |
| Detection Method | Agglutination |
| Sample Type | Human Serum |
| Sensitivity | 200 IU/mL |
| Disposable | Single-use |